by Yunir Gataullin, Consultant – Space Projects, Darius Pro
Introduction
This analysis will examine the company’s assets, expertise, capabilities, and intangible assets, including the internal resources of the company, with the objective of determining the strategic advantage (Lubis, 2022). Thales Alenia Space is a joint venture between the Thales Group (67% ownership) and Leonardo (33% ownership). It specializes in space exploration technologies and satellite systems. With contributions to various historic projects, including Galileo, Copernicus, and the International Space Station, it is among the top firms in the European space sector.
Company Overview
Name: Thales Alenia Space, www.thalesaleniaspace.com
Products and Services: Satellites, payloads, and orbital infrastructure are designed and built by Thales Alenia Space. Additionally, it plays a significant role in initiatives like telecommunications networks, navigation (Galileo), and Earth observation.
Latest achievements
According to the Thales Reports (2024), the Aerospace segment’s order book was €9.3 billion as of December 31, 2023, up 2% from 2022. Thales Alenia Space recorded new commercial successes in Earth Observation (IRIDE, I‑HAB) and Satellite Navigation (Galileo). The numbers do not include the Defence & Security segment.

The company has outlined a strategic plan to enhance this margin to 7% by 2028. (Spaceintel, 2024). This improvement is expected to result from organizational restructuring, reduced research and development expenditures as new products enter the market, and growth driven by its exploration and services operations.
Tangible and Intangible Resources
Tangible Resources
Thales Alenia Space runs state-of-the-art factories, such as high-technology production lines for integration of complex satellite systems, whose production lines for satellites are fitted with the most recent technology that enables their products to meet quality standards (European Space Agency, 2024). Advanced equipment for scientific research, Earth observation, telecommunications, and other uses is also covered. For the Ground Segment, a strong infrastructure facilitates data processing and satellite operations. Additionally, the Global Supply Chain is well-established, with the network facilitating the smooth acquisition and distribution of components.
Intangible Resources
Resources equally important to Thales are the intangible ones. Among these are its IP in satellite communication and aerospace systems, the high quality of its workforce, partnership relations with space agencies like ESA, and a reputation for reliability and innovation (Barney, 1991). Also, their well designed algorithms and software for satellite navigation, especially those concerning the Galileo project, constitute a significant competitive advantage (Thales Group, 2024).
Suggestions
Build: Thales Alenia Space should expand its R&D efforts in autonomous satellite systems, quantum communication, and AI-driven space applications to maintain leadership in cutting-edge technologies (Kennedy, 2020).
Preserve: It has to keep developing its employees through training and retain its partnerships with ESA, NASA, and other agencies. It also needs to preserve its brand reputation through good products and services on the market at all times (Barney, 1991).
Heterogeneous and Immobile Resources
Heterogeneous Resources
Heterogeneous resources are those unique to Thales, setting it apart from competitors. Examples include:
Satellite Communication Expertise:Particularly with regard to high-performance payloads for Galileo and Copernicus, Thales Alenia Space has established a solid reputation in the field of satellite communication. The European Space Agency has identified Thales as a prominent provider in this field, demonstrating that this specialization is a considerable competitive advantage (European Space Agency, 2024).
Research and Development Capabilities: Skills in Research and Development are equally remarkable at Thales. Their constant innovation in defence and aerospace technologies has created unique differentiators, especially in the European space industry (Kennedy, 2020).
Immobile Resources
Immobile resources are those that cannot be easily transferred or replicated. Gordon (2024). The following resources stop competitors from easily replicating resources of Thales Alenia Space:
Long-Term Partnerships: The company has established long-term relationships with ESA, NASA and European governments, which are not easily transferable (Thales Group, 2024). They have access to prestigious programs and funding opportunities.
Brand Reputation: The company has built decades of trust through successful projects, which has established a high level of credibility that competitors cannot quickly duplicate (Barney, 1991).
Why these resources matter
These resources are unique to Thales Alenia due to the years of expertise, trust, and collaboration required to build them. For example, their strong relationship with ESA ensures access to large-scale projects that competitors struggle to secure (European Space Agency, 2024).
VRIO Analysis of Thales Alenia Space
The VRIO framework evaluates resources based on their Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization. Below is an analysis of Thales Alenia resources:
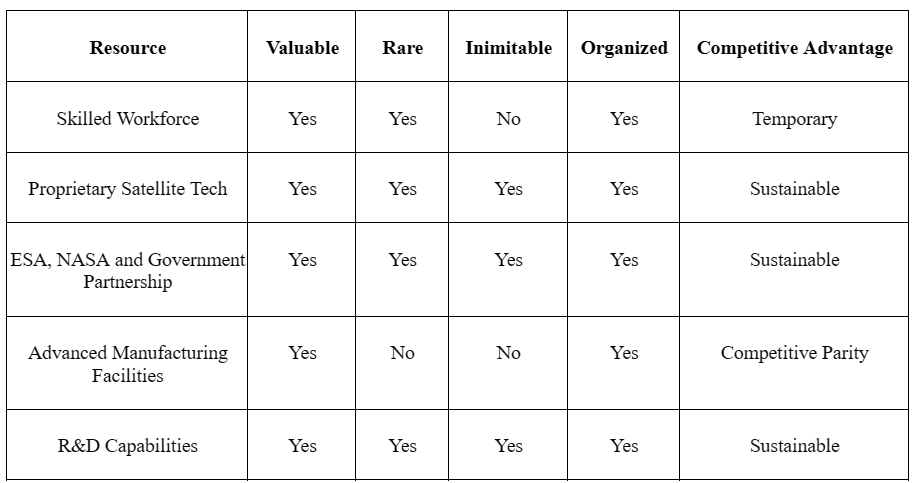
Discussion of Differential Performance
Thales Alenia Space’s competitive edge comes from its proprietary satellite technology, strong partnerships, and innovative R&D efforts. This signifies that the resources, as identified through the VRIO analysis (e.g., ESA relationship, R&D capabilities), are capable of attaining sustained performance. This is feasible due to the fact that competitors are confronted with significant barriers to imitation, as postulated by Porter (2008). Furthermore, the company’s differential performance in continuous resources is reinforced by the continuous adaptation to dynamic demands set by the industry.
Recommendations and Conclusion
The resource-based view (RBV) clearly illustrates how Thales Alenia Space’s internal resources support its strategic success in a market that is fiercely competitive and changing quickly. As a leader in the European and international space industries, the company has done so by utilizing both tangible resources, like state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and state-of-the-art R&D infrastructure, and intangible resources, like its proprietary satellite technology, long-standing partnerships with ESA and NASA, and a solid reputation for innovation. These assets are essential to the business’s ability to maintain a competitive edge.
The resource-based view highlights how internal resources drive Thales Alenia strategic success. In my opinion, Thales Alenia should:
- Focus on Proprietary Innovation: The company will be able to continue satisfying the ever-changing needs of the space industries by stepping up research and development into cutting-edge areas including autonomous satellite systems, quantum communication, and AI-driven space applications. Such a commitment to innovation ensures Thales Alenia continues to stay at the leading edge of technological developments and continues to stand out from the competition.
- Expand Strategic Partnerships: Another important direction of development is strategic partnerships. The company’s portfolio could be diversified by international space agencies, private sector players, and emerging markets, thus protecting it from market fluctuations. Closer relations with respected partners, such as ESA and NASA, will allow the company to take part in prestigious programs and receive corresponding funding, while building trust and cooperation that will be difficult for competitors to compete with.
- Improvement of EBIT margins: According to Thales Reports (2024), it looks like the company had a good plan for improving EBIT margins, which evinced a proactive approach towards financial vulnerabilities. Thales Alenia Space targets financial sustainability and operational efficiency through the restructuring of operational activities, research and development expenditure optimization, and the leveraged growth of exploration and services. This, plus the focus on exploiting resources that are truly unique, places the company in an advantageous position for success within the frame of an innovative and flexible industry.
By supporting its tangible and intangible assets and capitalizing on its sustainable competitive advantages, Thales Alenia will continue to create an exemplary case in the space industry.
References
Barney, J. B. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management. Retrieved from https://josephmahoney.web.illinois.edu/BA545_Fall%202022/Barney%20(1991).pdf
Darius Space (2024). How AI is advancing space applications. Retrieved from https://darius.space/
European Space Agency. (2024). Galileo Program Overview. Retrieved from https://defence-industry-space.ec.europa.eu/eu-space/galileo-satellite-navigation_en
Gordon J.M. (2024) Resource Based View (Strategy) – Explained. Retrieved from https://thebusinessprofessor.com/en_US/business-management-amp-operations-strategy-entrepreneurship-amp-innovation/resource-based-view-strategy-explained
Kennedy, R. (2020). Strategic management. Virginia Tech Publishing. Retrieved from https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/99282/Strategic-Management.pdf?sequence=22&isAllowed=y
Lubis (2022). Resource Based View (RBV) in Improving Company Strategic Capacity Retrieved from https://journal.lifescifi.com/index.php/RH/article/view/85
Porter, M. E. (2008). The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5581445_The_Five_Competitive_Forces_That_Shape_Strategy
Spaceintel (2024). Thales Alenia Space: Here’s how we grow EBIT to 7% in 2028 from 1% in 2023, not counting Iris2, and without a merger. https://www.spaceintelreport.com/thales-alenia-space-heres-how-we-grow-ebit-to-7-in-2028-from-1-in-2023-not-counting-iris2-and-without-a-merger/
Thales Group. (2024). Thales seizes control of ESA demonstration satellite in first cybersecurity exercise of its kind. Retrieved from https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/worldwide/security/press_release/thales-seizes-control-esa-demonstration-satellite-first
Thales Reports (2024), Retrieved from https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/group/investors/press_release/thales-reports-its-2024-half-year-results
